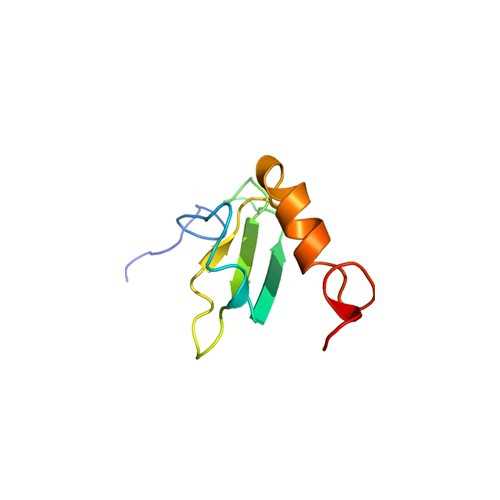
Human Vitronectin N-GST (heparin-binding domain deletion)
This VN fragment contains a deletion of 12 residues (amino acids K347–G358) in the heparin binding domain which are essential to its function. Binding and cell adhesion studies indicate that a deletion of these amino acids results in a loss of soluble vitronectin binding to adherent cells as well as loss of syndecan dependent cell adhesion. It is expressed as a GST-tagged fusion protein in E. coli, liberated from inclusion bodies by urea treatment, and purified over heparin–agarose.
Vitronectin (VN) is a 75-kDa adhesive glycoprotein that also plays a role in regulating several proteolytic enzyme cascades including complement, thrombosis, and fibrinolysis. Several distinct, biologically active conformations of VN are known to exist. In the blood, VN circulates in a monomeric form. High molecular mass oligomers of VN are found within the extracellular matrix (ECM)1 and in platelet releasate. The interaction of vitronectin with thrombin–antithrombin III complexes, plasminogen activator inhibitor, or with chemical or thermal denaturants results in conformational changes that lead to VN multimerization. These conformational changes may be important for VN activity as the multimeric form of VN preferentially binds to v 3 and IIb 3 integrins, urokinase receptors, plasminogen activator inhibitor, and glycosaminoglycans. The interaction of multimeric VN with these ligands affects a number of functions including cell adhesion and spreading, cell migration, inflammation, and hemostasis.
From the laboratory of Denise C. Hocking, PhD, University of Rochester Medical Center.
 Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
This VN fragment contains a deletion of 12 residues (amino acids K347–G358) in the heparin binding domain which are essential to its function. Binding and cell adhesion studies indicate that a deletion of these amino acids results in a loss of soluble vitronectin binding to adherent cells as well as loss of syndecan dependent cell adhesion. It is expressed as a GST-tagged fusion protein in E. coli, liberated from inclusion bodies by urea treatment, and purified over heparin–agarose.
Vitronectin (VN) is a 75-kDa adhesive glycoprotein that also plays a role in regulating several proteolytic enzyme cascades including complement, thrombosis, and fibrinolysis. Several distinct, biologically active conformations of VN are known to exist. In the blood, VN circulates in a monomeric form. High molecular mass oligomers of VN are found within the extracellular matrix (ECM)1 and in platelet releasate. The interaction of vitronectin with thrombin–antithrombin III complexes, plasminogen activator inhibitor, or with chemical or thermal denaturants results in conformational changes that lead to VN multimerization. These conformational changes may be important for VN activity as the multimeric form of VN preferentially binds to v 3 and IIb 3 integrins, urokinase receptors, plasminogen activator inhibitor, and glycosaminoglycans. The interaction of multimeric VN with these ligands affects a number of functions including cell adhesion and spreading, cell migration, inflammation, and hemostasis.
From the laboratory of Denise C. Hocking, PhD, University of Rochester Medical Center.
 Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
| Product Type: | Protein |
| Name: | Recombinant Human Vitronectin (heparin binding domain deletion); amino acids D1-L459 with T347-K358 deleted |
| Accession ID: | P04004 |
| Source: | Human protein expressed in E. coli DH5 alpha carrying the cloned gene in pGEX-2T |
| Molecular Weight: | 77118.8 Da |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | DQESCKGRCTEGFNVDKKCQCDELCSYYQSCCTDYTAECKPQVTRGDVFTMPEDEYTVYDDGEEKNNATVHEQVGGPSLTSDLQAQSKGNPEQTPVLKPEEEAPAPEVGASKPEGIDSRPETLHPGRPQPPAEEELCSGKPFDAFTDLKNGSLFAFRGQYCYELDEKAVRPGYPKLIRDVWGIEGPIDAAFTRINCQGKTYLFKGNQYWRFEDGVLDPDYPRNISDGFDGIPDNVDAALALPAHSYSGRERVYFFKGKQYWEYQFQHQPSQEECEGSSLSAVFEHFAMMQRDSWEDIFELLFWGRTSAGTRQPQFISRDWHGVPGQVDAAMAGRIYISGMAPRPSLGYRSQRGHSRGRNQNSRRPSRAMWLSLFSSEESNLGANNYDDYRMDWLVPATCEPIQSVFFFSGDKYYRVNLRTRRVDTVDPPYPRSIAHYWLGCPAPGHL |
| Fusion Tag(s): | GST, N-terminal |
| Purity: | > 60% by SDS-PAGE |
| Buffer: | Solution in PBS |
| Concentration: | 0.6mg/mL |
| Storage: | Store at -80C |
| Shipped: | Dry ice |
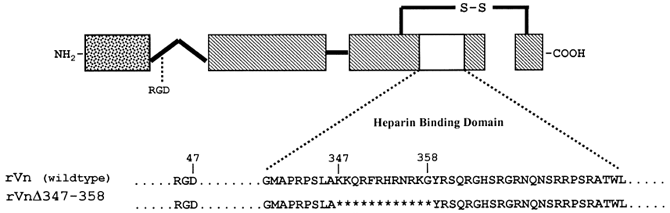 |
| Schematic of recombinant vitronectins and fusion proteins. Regions subjected to modification are aligned for comparison, with the pertinent residue numbers indicated across the top. rVn represents the recombinant wildtype form of vitronectin. rVn delta 347358 is a fulllength form of recombinant vitronectin containing a deletion of residues K347G358 within the heparin binding domain. Adapted from: Wilkins-Port, C.E., Sanderson, R.D., Tominna-Sebald, E.T., and McKeown-Longo, P.J. (2003) Vitronectin's basic domain is a syndecan ligand which functions in trans to regulate vitronectin turnover. Cell Commun. Adhes. 10: 85-103 |
- Wilkins-Port, C.E., Sanderson, R.D., Tominna-Sebald, E.T., and McKeown-Longo, P.J. (2003) Vitronectin's basic domain is a syndecan ligand which functions in trans to regulate vitronectin turnover. Cell Commun. Adhes. 10: 85-103
If you publish research with this product, please let us know so we can cite your paper.