WT-apoCA-tagRFP Biosensor Protein
WT-apoCA-tagRFP Biosensor Protein is a fluorescence-based biosensor with highest sensitivity for extracellular use.
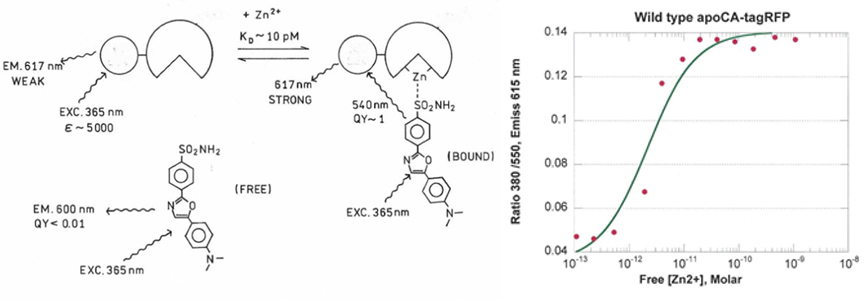
Together with 4-(dimethylaminophenyl)benzoxazolyl sulfonamide, one can measure free zinc in aqueous solution at concentrations in the picomolar range (PMID 22430627, PMID 19152866, PMID: 17163650). The protein is a fusion protein of wild type apocarbonic anhydrase together with tagRFP. It is an example of an excitation ratiometric sensors, which makes accurate, reproducible calibration simple and minimizes most artifacts: the principle is illustrated below. When zinc is not bound, the 4-(dimethylaminophenyl)benzoxazolyl sulfonamide does not bind and emission at 610 nm (or other suitable wavelength) is weak when excited at 365 nm. However, when zinc binds to the carbonic anhydrase active site, the sulfonamide can now bind with a substantial increase in quantum yield, and efficiently transfers its energy to the attached tagRFP, which then emits in the red. Directly exciting the tagRFP at 555 nm enables one to normalize the UV-excited Zn-bound form against the total tagRFP as an excitation ratio.
Read plog post from Dr. Richard Thompson at Pokegama Technologies, Improving Zinc Ion Quantitation with Unique Biosensor Proteins and Buffers.
WT-apoCA-tagRFP Biosensor Protein is a fluorescence-based biosensor with highest sensitivity for extracellular use.
Together with 4-(dimethylaminophenyl)benzoxazolyl sulfonamide, one can measure free zinc in aqueous solution at concentrations in the picomolar range (PMID 22430627, PMID 19152866, PMID: 17163650). The protein is a fusion protein of wild type apocarbonic anhydrase together with tagRFP. It is an example of an excitation ratiometric sensors, which makes accurate, reproducible calibration simple and minimizes most artifacts: the principle is illustrated below. When zinc is not bound, the 4-(dimethylaminophenyl)benzoxazolyl sulfonamide does not bind and emission at 610 nm (or other suitable wavelength) is weak when excited at 365 nm. However, when zinc binds to the carbonic anhydrase active site, the sulfonamide can now bind with a substantial increase in quantum yield, and efficiently transfers its energy to the attached tagRFP, which then emits in the red. Directly exciting the tagRFP at 555 nm enables one to normalize the UV-excited Zn-bound form against the total tagRFP as an excitation ratio.
Read plog post from Dr. Richard Thompson at Pokegama Technologies, Improving Zinc Ion Quantitation with Unique Biosensor Proteins and Buffers.
| Product Type: | Protein |
| Name: | wt-apoCA-tagRFP biosensor protein |
| Extinction Coefficient: | ε555 nm = 100,001 |
| Molecular Weight: | 60,000 Da |
| Variant MPN: | T-0005 |
| Format: | Solution in pH 7.5 buffer |
| Purity: | >95% |
| Tested Applications: | Extracellular measurement and imaging of free zinc ion at picomolar levels |
| Comments: | Fluorescent-labeled zinc free apoprotein; fluorescent label excitation maximum 555 nm, preferred emission wavelength 612 nm |
| Storage: | +4C |
| Shipped: | Cold packs |
- B. J. McCranor, R. A. Bozym, M. Vitolo, C. A. Fierke, L. Bambrick, B. Polster, G. Fiskum, and R. B. Thompson, "Quantitative imaging of mitochondrial and cytosolic free zinc levels in an in vitro model of ischemia/reperfusion" Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes 44(2) 253 - 263 (2012). DOI: 10.1007/s10863-012-9427-2 PMID 22430627 NIHMS382081
- D. Wang, T. K. Hurst, R. B. Thompson, and C. A. Fierke ÒGenetically Encoded Ratiometric Biosensors to Measure Intracellular Exchangeable Zinc in Escherichia coliÓJ. Biomed. Opt. 16(8) 087011/1-11 (2011) [DOI: 10.1117/1.3613926. PMID: 21895338 PMCID: PMC3166341.
- R.A. Bozym, T. Hurst, N. Westerberg, A.V. Stoddard, C.A. Fierke, C.J. Frederickson, R.B. Thompson, ÒDetermination of zinc using carbonic anhydrase-based fluorescence biosensors,Ó in Methods in Enzymology: Fluorescence Spectroscopy Vol. 450 (L. Brand and M.L. Johnson, editors) New York: Elsevier, pp 279-301 (2008). PMID 19152866.
- R. A. Bozym, A. K. Stoddard, C. A. Fierke, and R. B. Thompson, ÒMeasuring picomolar exchangeable zinc in PC-12 cells using a ratiometric fluorescence biosensor,Ó ACS Chemical Biology1(2) 103 Ð 111 (2006) PMID: 17163650.
- R. B. Thompson, M. L. Cramer, R. Bozym, and C. A. Fierke, ÒExcitation ratiometric fluorescent biosensor for zinc ion at picomolar levels,Ó J. Biomed. Optics7 (4), 555 - 506 (2002). PMID 1242112
If you publish research with this product, please let us know so we can cite your paper.