Anti-eIF4G1 [4GRH09] Antibody
This antibody was raised in mice against human eukaryotic initiation factor 4G (eIF4G1) that was expressed in and purified from Sf9 cells.
The initiation of translation is an important biological event and a variety of factors contribute to this process. Members of the Eukaryotic initiation factor 4G (eIF4G) translation factor family bind to the 5' mRNA cap and unwind the mRNA secondary structure.
eIF4G (eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma) is a protein involved in bringing mRNA to the ribosome for translation, in general based on mRNA's distinctive guanosine cap.The amino-terminal portion of eIF4G physically associates with eIF4E to stimulate the binding of eIF4E to the mRNA cap structure. eIF4G also interacts with eIF3 and eIF4A and serves as an adaptor molecule in the eIF4 complex. Moreover, eIF4G plays a role in internal ribosomal entry site (IRES)-mediated initiation of translation.
From the laboratory of Scot R. Kimball, PhD, Penn State College of Medicine
 Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
This antibody was raised in mice against human eukaryotic initiation factor 4G (eIF4G1) that was expressed in and purified from Sf9 cells.
The initiation of translation is an important biological event and a variety of factors contribute to this process. Members of the Eukaryotic initiation factor 4G (eIF4G) translation factor family bind to the 5' mRNA cap and unwind the mRNA secondary structure.
eIF4G (eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma) is a protein involved in bringing mRNA to the ribosome for translation, in general based on mRNA's distinctive guanosine cap.The amino-terminal portion of eIF4G physically associates with eIF4E to stimulate the binding of eIF4E to the mRNA cap structure. eIF4G also interacts with eIF3 and eIF4A and serves as an adaptor molecule in the eIF4 complex. Moreover, eIF4G plays a role in internal ribosomal entry site (IRES)-mediated initiation of translation.
From the laboratory of Scot R. Kimball, PhD, Penn State College of Medicine
 Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
| Product Type: | Antibody |
| Name: | Anti-eIF4G monoclonal antibody (4GRH09) |
| Accession ID: | Q04637 |
| Host: | Mouse |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Clonality: | Monoclonal |
| Clone Name: | 4GRH09 |
| Specificity: | This antibody recognizes human eIF4G1 |
| Immunogen: | Whole protein |
| Format: | Liquid |
| Purification Method: | HiTrap Protein G HR chromatography |
| Tested Applications: | Western blotting and IP. |
| Concentration: | 1mg/mL |
| Amount: | 100uL |
| Storage: | Store at 4C |
| Shipped: | Cold packs |
| Western Blot: The blot shown on the right was incubated with anti-eIF4G1 antibody at a 1:3,000 dilution followed by secondary antibody (Bethyl Laboratory) at a 1:10,000 dilution. The blot was developed with ECL reagent. Equal amounts of protein from HEK293 (human), C2C12 (mouse), and Rat 2 (rat) were analyzed. | 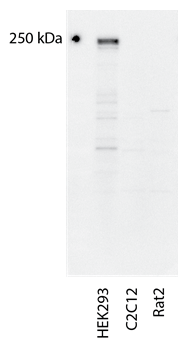 |
- Baum, JI et al. Glucagon acts in a dominant manner to repress insulin-induced mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 signaling in perfused rat liver. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 297(2): E410 - 5. 2009.
If you publish research with this product, please let us know so we can cite your paper.

![Anti-eIF4G1 [4GRH09] Antibody Anti-GFP (Chicken-Standard) Antibody](https://www.kerafast.com/MediaStorage/Product/Images/Medium/113_200120200125541120D.jpg)
