Polyphosphate, Long Chain (p700)
This polyphosphate (High MW, p700) is heterogeneous in size, with approximate polymer lengths ranging from ~200-1,300 phosphate units; modal size is about 700 phosphate units.
Polyphosphate, a linear polymer of inorganic orthophosphate, which is widespread in living organisms and which plays diverse roles in biology, has recently been shown to be a potent modulator of the human blood clotting system. Its procoagulant activity is dependent on polymer length; this high MW polyphosphate preparation has very high specific activity in plasma clotting assays.
In addition to being a useful tool for plasma clotting assays, polyphosphate is can be used to study bacterial growth, virulence, and bacterial membrane function.
Also available:
- Polyphosphate, Medium Chain (p100)
- Biotinylated Polyphosphate, Medium Chain (p100)
- Biotinylated Polyphosphate, Long Chain (p700)
From the laboratory of James H. Morrissey, PhD, University of Michigan.
This polyphosphate (High MW, p700) is heterogeneous in size, with approximate polymer lengths ranging from ~200-1,300 phosphate units; modal size is about 700 phosphate units.
Polyphosphate, a linear polymer of inorganic orthophosphate, which is widespread in living organisms and which plays diverse roles in biology, has recently been shown to be a potent modulator of the human blood clotting system. Its procoagulant activity is dependent on polymer length; this high MW polyphosphate preparation has very high specific activity in plasma clotting assays.
In addition to being a useful tool for plasma clotting assays, polyphosphate is can be used to study bacterial growth, virulence, and bacterial membrane function.
Also available:
- Polyphosphate, Medium Chain (p100)
- Biotinylated Polyphosphate, Medium Chain (p100)
- Biotinylated Polyphosphate, Long Chain (p700)
From the laboratory of James H. Morrissey, PhD, University of Michigan.
| Catalog Number | Product | DataSheet | Size | AVAILABILITY | Price | Qty |
|---|
Not seeing the size you're looking for? For custom sizes or bulk pricing, please contact us for a quote.
| Product Type: | Small Molecule |
| Name: | Polyphosphate, Long Chain (p700) |
| Chemical Formula: |
Nan+2PnO3n +1 or Lin+2PnO3n +1 n = the average number of phosphorus (P) atoms in the chain (Up to 10% of counterions may be Li+ rather than Na+) |
| Molecular Weight: | Heterogeneous; Number average ~113 kDa; Range ~10 kDa to 208 kDa |
| Format: | Lyophilized |
| Purity: | <1% monophosphate |
| Buffer: | 50mM MES, pH 6.0, 1mM EDTA (also see information in the product documentation) |
| Solubility: | At least 1 M in water; <1 mM in buffers containing divalent metals (make intermediate dilutions in metal-free buffers) |
| Concentration: | When reconstituted: 1 M (phosphate monomer) NOTE: To estimate the polymer concentration, divide the phosphate monomer concentration by the modal polymer length |
| Size Distribution: | Mode of n: 1000-1300 (as measured by migration on PAGE) |
| Storage: |
Dry material should be stored at room temperature (or lower) with dessication. Once reconstituted: - Stable at least 12 hours at room temperature - Stable at least 72 hours at 4C - Store long-term at -80C - Aliquot for repeated use, avoiding repeated freeze-thaw cycles - Do not store in the presence of divalent metal ions |
| Shipped: | Ambient temperature |
Size Distribution
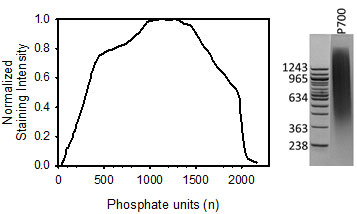
Polyphosphate has limited solubility in the presence of divalent metal ions, so make intermediate dilutions in water, or in buffers without divalent metals or polyphosphate-binding proteins.
Reconstitution:
1 - Centrifuge 100mg tube 1 min at 1000 x g to pellet material in bottom of tube.
2 - Reconstitute in 1.0 mL purified water to make a solution of 1 M phosphate (= 102 mg/mL polyP).
NOTE: May be reconstituted in larger volumes to make a more dilute solution as needed.
- Morrissey JH, Choi SH, and Smith S.A. Polyphosphate: an ancient molecule that links platelets, coagulation and inflammation. Blood 119:5972-5979, 2012.
- Rao NN, Gómez-García MR, and Kornberg A. Inorganic polyphosphate: essential for growth and survival. Annu Rev Biochem. 78:605-647, 2009.
- Dinarvand P, Hassanian SM, Qureshi SH, Manithody C, Eissenberg JC, Yang L, Rezaie AR. Polyphosphate amplifies proinflammatory responses of nuclear proteins through interaction with receptor for advanced glycation end products and P2Y1 purinergic receptor. Blood. 2014 Feb 6;123(6):935-45.
- Osbourne DO, Soo VW, Konieczny I, Wood TK. Polyphosphate, cyclic AMP, guanosine tetraphosphate, and c-di-GMP reduce in vitro Lon activity. Bioengineered. 2014 Jul-Aug;5(4):264-8. View Article
- Gray MJ, Wholey WY, Wagner NO, Cremers CM, Mueller-Schickert A, Hock NT, Krieger AG, Smith EM, Bender RA, Bardwell JC, Jakob U. Polyphosphate is a primordial chaperone. Mol Cell. 2014 Mar 6;53(5):689-99.
- Jablonka W, Kotsyfakis M, Mizurini DM, Monteiro RQ, Lukszo J, Drake SK, Ribeiro JM, Andersen JF. Identification and Mechanistic Analysis of a Novel Tick-Derived Inhibitor of Thrombin. PLoS One. 2015 Aug 5;10(8):e0133991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133991. View Article
- Chuang YM, Bandyopadhyay N, Rifat D, Rubin H, Bader JS, Karakousis PC. Deficiency of the novel exopolyphosphatase Rv1026/PPX2 leads to metabolicdownshift and altered cell wall permeability in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. MBio. 2015 Mar 17;6(2):e02428. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02428-14. View Article
- Alvarenga PH, Xu X, Oliveira F, Chagas AC, Nascimento CR, Francischetti IM, Juliano MA, Juliano L, Scharfstein J, Valenzuela JG, Ribeiro JM, Andersen JF. Novel family of insect salivary inhibitors blocks contact pathway activation by binding to polyphosphate, heparin, and dextran sulfate. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Dec;33(12):2759-70. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302482. PubMed PMID: 24092749; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4191670. View Article
- Morrissey JH. Poly-P as Modulator of Hemostasis, Thrombosis, and Inflammation. Blood 2017 130:SCI-1.
- Rivero M, Torres-Paris C, Muñoz R, Cabrera R, Navarro CA, Jerez CA. Inorganic Polyphosphate, Exopolyphosphatase, and Pho84-Like Transporters May Be Involved in Copper Resistance in Metallosphaera sedula DSM 5348(T). Archaea. 2018 Mar 5;2018:5251061. View Article
- Biswas I, Panicker SR, Cai X, Mehta-D'souza P, Rezaie AR. Inorganic Polyphosphate Amplifies High Mobility Group Box 1-Mediated Von Willebrand Factor Release and Platelet String Formation on Endothelial Cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Jun 21. View Article
- Li L, Khong ML, Lui ELH, Mebarek S, Magne D, Buchet R, Tanner JA. Long-chain polyphosphate in osteoblast matrix vesicles: Enrichment and inhibition of mineralization. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2019 Jan;1863(1):199-209. View Article
- Cordeiro CD, Ahmed MA, Windle B, Docampo R. NUDIX hydrolases with inorganic polyphosphate exo- and endopolyphosphatase activities in the glycosome, cytosol and nucleus of Trypanosoma brucei. Biosci Rep. 2019 May 17;39(5). pii: BSR20190894. View Article
- An J, Cho J. Catalytic properties of wheat phytase that favorably degrades long-chain inorganic polyphosphate. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2019 May 27. View Article
- Negreiros RS, Lander N, Huang G, Cordeiro CD, Smith SA, Morrissey JH, Docampo R. Inorganic polyphosphate interacts with nucleolar and glycosomal proteins in trypanosomatids. Mol Microbiol. 2018 Dec;110(6):973-994. View Article
- Negreiros RS, Lander N, Huang G, et al. Inorganic polyphosphate interacts with nucleolar and glycosomal proteins in trypanosomatids. Mol Microbiol. 2018;110(6):973-994. View article
- Gross MH, Konieczny I. Polyphosphate induces the proteolysis of ADP-bound fraction of initiator to inhibit DNA replication initiation upon stress in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48(10):5457-5466. View article
If you publish research with this product, please let us know so we can cite your paper.


