Goat Anti-GIRK2 / KCNJ6 Antibody
This goat IgG polyclonal antibody was generated against peptide sequence C-SSKLNQHAELET from the C Terminus of G protein-activated inward rectifier potassium channel 2 (GIRK2) and recognizes human GIRK2.
Highlights:
- Reacts with human GIRK2
- Suitable for Peptide ELISA and Western Blot applications
- Mutations are associtated with Keppen-Lubinsky Syndrome
G protein-activated inward rectifier potassium channel 2 (GIRK2) is a member of the G protein-coupled inwardly-rectifying potassium channel family of inward rectifier potassium channels. This potassium channel has a greater tendency to allow potassium to enter the cell than leave the cell. GIRK2 participates in many physiological processes by forming multimeric complexes with other channel proteins and is present at high levels in most mammalian tissues. Mutations in GIRK2 are associated with Keppen-Lubinsky Syndrome.
This goat IgG polyclonal antibody was generated against peptide sequence C-SSKLNQHAELET from the C Terminus of G protein-activated inward rectifier potassium channel 2 (GIRK2) and recognizes human GIRK2.
Highlights:
- Reacts with human GIRK2
- Suitable for Peptide ELISA and Western Blot applications
- Mutations are associtated with Keppen-Lubinsky Syndrome
G protein-activated inward rectifier potassium channel 2 (GIRK2) is a member of the G protein-coupled inwardly-rectifying potassium channel family of inward rectifier potassium channels. This potassium channel has a greater tendency to allow potassium to enter the cell than leave the cell. GIRK2 participates in many physiological processes by forming multimeric complexes with other channel proteins and is present at high levels in most mammalian tissues. Mutations in GIRK2 are associated with Keppen-Lubinsky Syndrome.
| Product Type: | Antibody |
| Name: | Goat Anti-GIRK2 / KCNJ6 Antibody |
| Alternative Name(s): | BIR1, KATP2, KCNJ7, KIR3.2 |
| Accession ID: | NP_002231.1 |
| Antigen: | GIRK2 / KCNJ6 |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Specificity: | GIRK2 / KCNJ6 |
| Immunogen: | CSSKLNQHAELET |
| Species Immunized: | Goat |
| Epitope: | C Terminus |
| Purification Method: | Purified from goat serum by ammonium sulphate precipitation followed by antigen affinity chromatography using the immunizing peptide |
| Buffer: | Supplied at 0.5 mg/ml in Tris saline, 0.02% sodium azide, pH7.3 with 0.5% bovine serum albumin. |
| Tested Applications: | Pep-ELISA, WB |
| Storage: | Aliquot and store at -20C. Minimize freezing and thawing. |
| Shipped: | Cold Packs |
Western Blot
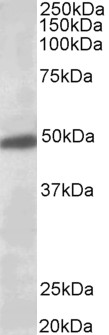
(0.5µg/ml) staining of human brain (Substantia Nigra) lysate (35µg protein in RIPA buffer). Detected by chemiluminescence.
If you publish research with this product, please let us know so we can cite your paper.