Anti-Influenza A Matrix 1 (M1) [1G1A12] Antibody
This mouse IgG1 mouse monoclonal antibody was raised against recombinant GST-M1 fusion protein and is specific for influenza A virus M1 protein.
Highlights:
- Reacts with M1 protein of Influenza virus
- Suitable for Western Blot and Immunofluorscence applications
The matrix 1 (M1) protein of the influenza A virus forms a coat inside the viral envelope and is the most abundant protein in virions. The M1 protein of influenza A virus has multiple regulatory functions during the infectious cycle and these include mediation of nuclear export of viral ribonucleoproteins, inhibition of viral transcription and a crucial role in virus assembly and budding.
From the laboratory of A*STAR Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology (IMCB) Monoclonal Antibody Unit.
This mouse IgG1 mouse monoclonal antibody was raised against recombinant GST-M1 fusion protein and is specific for influenza A virus M1 protein.
Highlights:
- Reacts with M1 protein of Influenza virus
- Suitable for Western Blot and Immunofluorscence applications
The matrix 1 (M1) protein of the influenza A virus forms a coat inside the viral envelope and is the most abundant protein in virions. The M1 protein of influenza A virus has multiple regulatory functions during the infectious cycle and these include mediation of nuclear export of viral ribonucleoproteins, inhibition of viral transcription and a crucial role in virus assembly and budding.
From the laboratory of A*STAR Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology (IMCB) Monoclonal Antibody Unit.
| Product Type: | Antibody |
| Antigen: | M1 protein of Influenza A virus |
| Accession ID: | P05777 |
| Molecular Weight: | 28 kDa |
| Isotype: | IgG1 |
| Clonality: | Monoclonal |
| Clone Name: | 1G1A12 |
| Reactivity: | Influenza A virus |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant GST-M1 fusion protein |
| Species Immunized: | Mouse |
| Buffer: | Cell culture supernatant |
| Tested Applications: | WB, IF, ELISA |
| Storage: | 80C |
| Shipped: | Cold Packs |
Immunofluorescence
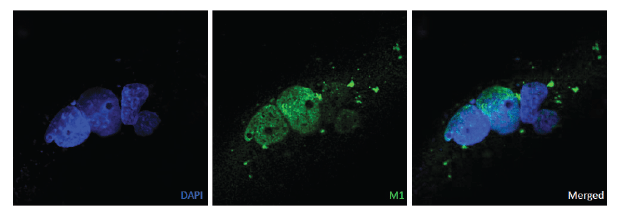
COS-7 cells were transfected with a plasmid containing the M1 open reading frame. Cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 and stained with anti-M1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) and followed by secondary goat antimouse FITC (lower panel).
From the laboratory of A*STAR Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology (IMCB) Monoclonal Antibody Unit.
- Barnwal B, Mok CK, Wu J, Diwakar MK, Gupta G, Zeng Q, Chow VT, Song J, Yuan YA, Tan YJ. A monoclonal antibody binds to threonine 49 in the non-structural 1 protein of influenza A virus and interferes with its ability to modulate viral replication. Antiviral Res. 2015 Apr;116:55-61.
If you publish research with this product, please let us know so we can cite your paper.

![Anti-Influenza A Matrix 1 (M1) [1G1A12] Antibody Anti-Influenza A Matrix 1 (M1) [1G1A12] Antibody](https://www.kerafast.com/MediaStorage/Product/Images/Medium/1746_2001202001270017450.jpg)
