Reversible Fluorescent Fe3+ Sensor (RPE)
RPE is a highly selective, sensitive and reversible off-on fluorescent Fe3+ sensor which can selectively image native Fe3+ in live cells.
Highlights:
- Allows for viewing of endogenous exchangeable Fe3+ pools at sub-cellular resolution
- Unique reversible "turn-on" property and high sensitivity
- Little interference from other biologically relevant metal ions
RPE is a highly sensitive, highly selective and reversible turn-on fluorescent Fe3+ sensor. The sensor readily detects endogenous chelatable Fe3+ in live human SH-SY5Y cells at subcellular resolution in real time. The sensor gives a distinct rapid and reversible fluorescence response upon the alteration of intracellular Fe3+ levels with little interference from other biologically relevant metal ions.
From the laboratory of Maolin Guo, PhD, University of Massachusetts Dartmouth.
RPE is a highly selective, sensitive and reversible off-on fluorescent Fe3+ sensor which can selectively image native Fe3+ in live cells.
Highlights:
- Allows for viewing of endogenous exchangeable Fe3+ pools at sub-cellular resolution
- Unique reversible "turn-on" property and high sensitivity
- Little interference from other biologically relevant metal ions
RPE is a highly sensitive, highly selective and reversible turn-on fluorescent Fe3+ sensor. The sensor readily detects endogenous chelatable Fe3+ in live human SH-SY5Y cells at subcellular resolution in real time. The sensor gives a distinct rapid and reversible fluorescence response upon the alteration of intracellular Fe3+ levels with little interference from other biologically relevant metal ions.
From the laboratory of Maolin Guo, PhD, University of Massachusetts Dartmouth.
Specifications
| Product Type: | Small Molecule |
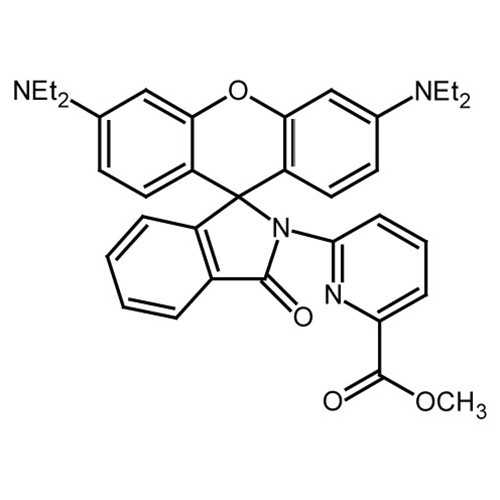
| Name: | Methyl 6-(3',6'-bis(diethylamino)-3-oxospiro[isoindoline-1,9'-xanthen]-2-yl)picolinate (RPE) |
| Chemical Formula: | C35H36N4O4 |
| Molecular Weight: | 576 |
| Format: | Off-white solid |
| Purity: | >95% |
| Solubility: | DMSO, DMF, EtOH, ACN, etc. |
| Spectral Information: | NMR, MS |
| Platform: | Fluorescence microscope |
| Compatible Cells: | Mammalian cells |
| Detection Method: | Fluorescence (excitation: 510-580 nm; emission: 550-700 nm) |
| Comments: | Avoid exposure to light; Suggested amount per experiment: 10 μM (or 0.1 μg) |
| Storage: | -20C to -80C |
| Shipped: | Dry ice |
Provider
From the laboratory of Maolin Guo, PhD, University of Massachusetts Dartmouth.
References
- Wei Y, Aydin Z, Zhang Y, Liu Z, Guo M. A turn-on fluorescent sensor for imaging labile Fe(3+) in live neuronal cells at subcellular resolution. Chembiochem. 2012 Jul 23;13(11):1569-73. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201200202. Epub 2012 Jun 26. PubMed PMID: 22736480.
If you publish research with this product, please let us know so we can cite your paper.