Anti-Phloem Sieve Element [RS6] Antibody
This mouse IgG monoclonal antibody was generated against sieve elements isolated from California shield leaf tissue cultures and recognizes an antigen in the Arabidopsis ecotype Columbia that is associated specifically with the plasma membrane of sieve elements, but not companion cells.
Arabidopsis early nodulin (ENOD)-like proteins are encoded by a multigene family composed of several types of structurally related phytocyanins that have a similar overall domain structure of an amino-terminal signal peptide, plastocyanin-like copper-binding domain, proline/serine-rich domain, and carboxy-terminal hydrophobic domain. The amino- and carboxy-terminal domains of the 21.5-kD sieve element-specific ENOD are posttranslationally cleaved from the precursor protein, resulting in a mature peptide of approximately 15 kD that is attached to the sieve element plasma membrane via a carboxy-terminal glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchor. Many of the Arabidopsis ENOD-like proteins accumulate in gametophytic tissues, whereas in both floral and vegetative tissues, the sieve element-specific ENOD is expressed only within the phloem.
From the laboratory of Richard D. Sjolund, PhD, University of Iowa.
 Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
This mouse IgG monoclonal antibody was generated against sieve elements isolated from California shield leaf tissue cultures and recognizes an antigen in the Arabidopsis ecotype Columbia that is associated specifically with the plasma membrane of sieve elements, but not companion cells.
Arabidopsis early nodulin (ENOD)-like proteins are encoded by a multigene family composed of several types of structurally related phytocyanins that have a similar overall domain structure of an amino-terminal signal peptide, plastocyanin-like copper-binding domain, proline/serine-rich domain, and carboxy-terminal hydrophobic domain. The amino- and carboxy-terminal domains of the 21.5-kD sieve element-specific ENOD are posttranslationally cleaved from the precursor protein, resulting in a mature peptide of approximately 15 kD that is attached to the sieve element plasma membrane via a carboxy-terminal glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchor. Many of the Arabidopsis ENOD-like proteins accumulate in gametophytic tissues, whereas in both floral and vegetative tissues, the sieve element-specific ENOD is expressed only within the phloem.
From the laboratory of Richard D. Sjolund, PhD, University of Iowa.
 Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
| Product Type: | Antibody |
| Antigen: | Early nodulin (ENOD)-like protein 9 (gene: At3g20570) |
| Accession ID: | AT3G20570.1 |
| Molecular Weight: | 15 kDa (mature peptide) |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Clonality: | Monoclonal |
| Clone Name: | RS6 |
| Reactivity: | Plant |
| Immunogen: | Sieve elements isolated from California shield leaf (Streptanthus tortuosus; Brassicaceae) tissue cultures |
| Species Immunized: | BALB/c Mouse |
| Purification Method: | Cell culture supernatant |
| Buffer: | Cell culture supernatant with 0.05% Sodium azide |
| Tested Applications: | Immunolocalization, Immunohistochemistry |
| Storage: | 4C short term, -80C long term (avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles) |
| Shipped: | Cold Packs |
Immunolocalization
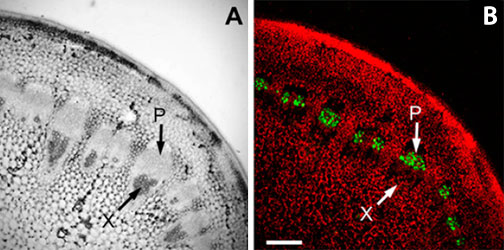
Confocal microscopy immunolocalization of the SE-ENOD. A, Brightfield image showing the phloem (P) and xylem (X) in fresh tissue vibratome sections (50100 um) of cauliflower stem. B, The RS6 monoclonal antibody labeled only the phloem in the vascular bundles of cauliflower stem sections (bar = 200um).
Adapted from: Khan JA, et al. Plant Physiol. 2007 Apr;143(4):1576-89.
- Khan JA, Wang Q, Sjölund RD, Schulz A, Thompson GA. An early nodulin-like protein accumulates in the sieve element plasma membrane of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2007 Apr;143(4):1576-89. Epub 2007 Feb 9.
- Stefan Hoth, Ruth Stadler, Norbert Sauer, and Ulrich Z. Hammes. Differential vascularization of nematode-induced feeding sites. PNAS Volume 105(34), 22617-12622, 2008.
- Kathrin Wippel and Norbert Sauer. Arabidopsis SUC1 loads the phloem in suc2 mutants when expressed from the SUC2 promoter. Journal of Experimental Botany (2011); Volume 63, Issue 2, Pp. 669-679.
- Birgit Absmanner, Ruth Stadler, Ulrich Z. Hammes. Phloem development in nematode-induced feeding sites: the implications of auxin and cytokinin. Front Plant Sci. 2013; 4: 241.
If you publish research with this product, please let us know so we can cite your paper.

![Anti-Phloem Sieve Element [RS6] Antibody Anti-Phloem Sieve Element [RS6] Antibody](https://www.kerafast.com/MediaStorage/Product/Images/Medium/987_200120200126299860.jpg)
