Anti-Adenylate Cyclase Toxin [3D1] Antibody
This IgG1 mouse antibody was generated against Bordetella pertussis Adenylate Cyclase toxin and recognizes the distal portion of the catalytic domain (amino acids 373-399).
Highlights:
- Reacts with the distal portion of the catalytic domain (amino acids 373-399)
- Suitable for Western Blot and Immunoprecipitation applications
Recombinant versions available from our sister company, Absolute Antibody:
- Manufactured using Absolute Antibody’s Recombinant Platform with variable regions (i.e., specificity) from the hybridoma 3D1.
Adenylate Cyclase Toxin (ACT or Cya A) is one of several virulence factors produced by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. This toxin invades eukaryotic cells and catalyzes the conversion of ATP into cyclic AMP (cAMP). This leads to inhibition of host cell immune function and macrophage death by apoptosis. The Adenylate Cyclase protein is composed of a catalytic domain (amino acids 1 to 400), a hydrophobic region (amino acids 500 to 700), a glycine/aspartate-rich repeat unit (amino acids 1000 to 1600), and the C-terminal domain (amino acids 1600-1706).
From the laboratory of Erik L. Hewlett, MD, University of Virginia.
This IgG1 mouse antibody was generated against Bordetella pertussis Adenylate Cyclase toxin and recognizes the distal portion of the catalytic domain (amino acids 373-399).
Highlights:
- Reacts with the distal portion of the catalytic domain (amino acids 373-399)
- Suitable for Western Blot and Immunoprecipitation applications
Recombinant versions available from our sister company, Absolute Antibody:
- Manufactured using Absolute Antibody’s Recombinant Platform with variable regions (i.e., specificity) from the hybridoma 3D1.
Adenylate Cyclase Toxin (ACT or Cya A) is one of several virulence factors produced by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. This toxin invades eukaryotic cells and catalyzes the conversion of ATP into cyclic AMP (cAMP). This leads to inhibition of host cell immune function and macrophage death by apoptosis. The Adenylate Cyclase protein is composed of a catalytic domain (amino acids 1 to 400), a hydrophobic region (amino acids 500 to 700), a glycine/aspartate-rich repeat unit (amino acids 1000 to 1600), and the C-terminal domain (amino acids 1600-1706).
From the laboratory of Erik L. Hewlett, MD, University of Virginia.
| Catalog Number | Product | DataSheet | Size | AVAILABILITY | Price | Qty |
|---|
| Product Type: | Antibody |
| Name: | Adenylate Cyclase Toxin [3D1] Antibody |
| Antigen: | Adenylate Cyclase Toxin (ACT, Cya A) |
| Accession ID: | J7QLC0 |
| Isotype: |
EG8001: IgG1 Recombinant versions: see product name |
| Clonality: | Monoclonal |
| Clone Name: | 3D1 |
| Reactivity: | Recognizes the distal portion of the catalytic domain (amino acids 373-399) |
| Immunogen: | Generated against Bordetella pertussis Adenylate Cyclase toxin |
| Species Immunized: | Mouse |
| Purification Method: | protein G |
| Buffer: |
EG8001: 0.1M Sodium Phosphate, pH 7.4, 0.15M NaCl, 0.05% (w/v) Sodium Azide Recombinant versions: PBS with 0.02% Proclin 300 |
| Tested Applications: | WB, IP |
| Concentration: | 1mg/mL |
| Comments: | Recommended for detection of Cya A of B. pertussis origin by Western Blotting (starting dilution 1:200, dilution range 1:100-1:1000) and immunoprecipitation [12 µg per 100500 µg of total protein (1 mL of cell lysate)]. |
| Storage: | -20C |
| Shipped: | Cold packs |
Proposed epitope map of the 3D1 mAb against AC toxin.
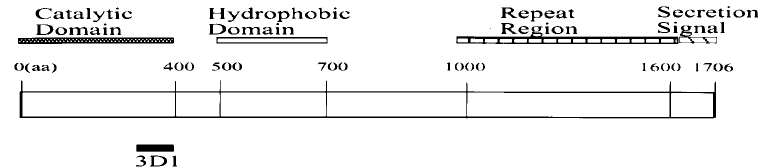
The linear sequence of AC toxin is shown along with its four major domains. Solid bars indicate theproposed epitope of the 3D1 MAb.
Adapted from: Lee SJ, Gray MC, Guo L, Sebo P, Hewlet EL. Epitope Mapping of Monoclonal Antibodies against Bordetella pertussis Adenylate Cyclase Toxin. Infect Immun. 67(5): 2090-5 (1999).
- Lee SJ, Gray MC, Guo L, Sebo P, Hewlet EL. Epitope Mapping of Monoclonal Antibodies against Bordetella pertussis Adenylate Cyclase Toxin. Infect Immun. 67(5): 2090-5 (1999).
- Herrou J, Willett JW, Crosson S. Structured and Dynamic Disordered Domains Regulate the Activity of a Multifunctional Anti-σ Factor. MBio. 2015 Jul 28;6(4):e00910. View Article
- Luebke JL, Eaton DS, Sachleben JR, Crosson S. Allosteric control of a bacterial stress response system by an anti-σ factor. Mol Microbiol. 2018 Jan;107(2):164-179. View Article
- Polak M, Zasada AA, Mosiej E, Krysztopa-Grzybowska K, Witkowski L, Rzeczkowska M, Piekarska K, Lutyńska A. Pertactin-deficient Bordetella pertussis isolates in Poland-a country with whole-cell pertussis primary vaccination. Microbes Infect. 2018 Dec 21. pii: S1286-4579(18)30193-X. View Article
- Joseph AM, Pohl AE, Ball TJ, Abram TG, Johnson DK, Geisbrecht BV, Shames SR. The Legionella pneumophila Metaeffector Lpg2505 (MesI) Regulates SidI-Mediated Translation Inhibition and Novel Glycosyl Hydrolase Activity. Infect Immun. 2020 Apr 20;88(5):e00853-19. View Article
If you publish research with this product, please let us know so we can cite your paper.

![Recombinant Anti-Adenylate Cyclase toxin [3D1], Mouse, IgG1 Product](https://www.kerafast.com/MediaStorage/Product/Images/Medium/5698_20210728085902513.jpg)
