Traptavidin Protein
Traptavidin is the S52G, R53D mutant of streptavidin, the high affinity biotin binding protein. Useful in various imaging, protein purification, and nano-assembly applications.
Highlights:
- 10-fold lower off-rate from biotin and biotin conjugates compared to streptavidin
- Increased thermal stability and mechanical stability of biotin binding compared to streptavidin
- Shows low non-specific binding to cells and DNA
Streptavidin binds biotin-conjugates with exceptional stability, but dissociation does occur and can be limiting in imaging, DNA amplification, and nanotechnology. This Traptavidin protein overcomes these limitations with a ~10-fold slower biotin off-rate, increased mechanical strength, and improved thermostability compared to streptavidin.
From the laboratory of Mark Howarth, PhD, University of Oxford.
Traptavidin is the S52G, R53D mutant of streptavidin, the high affinity biotin binding protein. Useful in various imaging, protein purification, and nano-assembly applications.
Highlights:
- 10-fold lower off-rate from biotin and biotin conjugates compared to streptavidin
- Increased thermal stability and mechanical stability of biotin binding compared to streptavidin
- Shows low non-specific binding to cells and DNA
Streptavidin binds biotin-conjugates with exceptional stability, but dissociation does occur and can be limiting in imaging, DNA amplification, and nanotechnology. This Traptavidin protein overcomes these limitations with a ~10-fold slower biotin off-rate, increased mechanical strength, and improved thermostability compared to streptavidin.
From the laboratory of Mark Howarth, PhD, University of Oxford.
| Catalog Number | Product | DataSheet | Size | AVAILABILITY | Price | Qty |
|---|
| Product Type: | Protein |
| Accession ID: | ADT80793.1 |
| Source: | Recombinant, expressed in E. coli |
| Molecular Weight: | 13.2 kDa (without boiling, traptavidin will run on SDS-PAGE as a tetramer and remain bound to biotin) |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | AEAGITGTWYNQLGSTFIVTAGADGALTGTYESAVGNAEGDYVLTGRYDSAPATDGSGTALGWTVAWKNNYRNAHSATTWSGQYVGGAEARINTQWLLTSGTTEANAWKSTLVGHDTFTKVKPSAAS |
| Fusion Tag(s): | None |
| Purity: | >98% by SDS PAGE (Purified from inclusion body refolding with selective ammonium sulfate precipitation and then iminobiotin-agarose affinity chromatography.) |
| Buffer: | Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.4; The protein is highly stable and should be compatible with a wide range of salts, ionic strengths and pH values (certainly 5-9), as well as DMF or DMSO up to 10%. |
| Concentration: | 3.36 mg/mL in PBS. |
| Comments: | 10-fold lower off-rate from biotin and biotin conjugates compared to streptavidin. Increased thermal stability and mechanical stability of biotin binding. |
| Storage: | -80°C, stable for 1-2 weeks when kept at 4°C (avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles) |
| Shipped: | Dry ice |
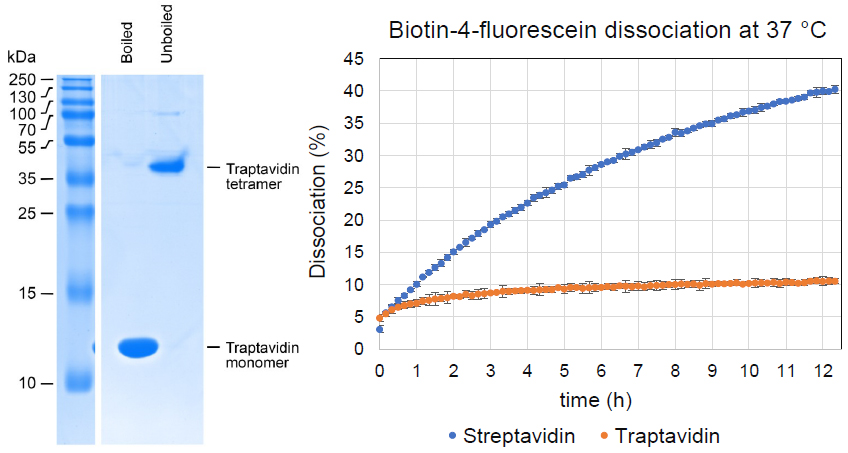
Traptavidin has a reduced on-rate compared to streptavidin, depending on the nature of the biotin conjugate; binding should still be rapid when working with high concentrations of biotinylated target, but for binding sub-micromolar concentrations of biotinylated target then longer should be allowed for binding than would be required for streptavidin.
- Theoretical pI for traptavidin: 5.1 (6.1 for streptavidin)
- Extinction coefficient (from ProtParam) at 280 nm: 41,940 M-1cm-1
- Chivers CE, Crozat E, Chu C, Moy VT, Sherratt DJ, Howarth M. A streptavidin variant with slower biotin dissociation and increased mechanostability. Nature Methods 2010 May;7(5):391-93.
- Chivers CE, Koner AL, Lowe ED, Howarth M. How the biotin-streptavidin interaction was made even stronger: investigation via crystallography and a chimaeric tetramer. Biochemical Journal 2011 Apr 1;435(1):55-63.
- Fu H, Jiang Y, Yang D, Scheiflinger F, Wong WP, Springer TA. Flow-induced elongation of von Willebrand factor precedes tension-dependent activation. Nat Commun. 2017 Aug 23;8(1):324. View Article
- Qing Y, Ionescu SA, Pulcu GS, Bayley H. Directional control of a processive molecular hopper. Science. 2018 Aug 31;361(6405):908-912. View Article
- Talreja D, Cashman SM, Dasari B, Kumar B, Kumar-Singh R. G-quartet oligonucleotide mediated delivery of functional X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein into retinal cells following intravitreal injection. Exp Eye Res. 2018 Oct;175:20-31. View Article
- Nguyen HC, Talledge N, McCullough J, et al. Membrane constriction and thinning by sequential ESCRT-III polymerization. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2020;27(4):392-399. View article
If you publish research with this product, please let us know so we can cite your paper.


