SACK-Xs 12(3) Neonatal Human Liver Stem Cells
Maintaining a population of adult stem cells (ASCs) allows one to exponentially propagate a population of cells in vitro, and induce differentiation when desired. This is possible with SACK cell strains and specified cell culture conditions.
SACK ASC Cell Properties
- Long-term propagation in xanthosine (Xs)-supplemented medium
- Suppressed asymmetric cell kinetics
- Express the epithelial stem cell biomarker LGR-5 and the liver stem cell biomarker EpCAM
- Xn-suppressed non-random sister chromatid segregation
- Quality controlled to determine number of actual stem cells More info
Differentiated progeny Cell Properties
- Xs-free medium, confluent monolayer, human serum-supplemented medium, serum reduction
- Loss of LGR5 and EpCAM expression
- Expression of hepatocyte-specific nuclear receptor PXR
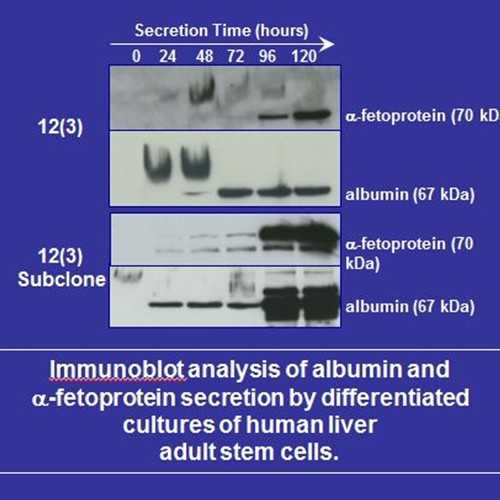
- Albumin secretion
- Alpha-fetoprotein secretion (indicates presence of hepatoblasts)
- Inducible cytochrome P450 activity (CYP3A4)
- Secretion of hepatocyte basement membrane proteins
Maintaining a population of adult stem cells (ASCs) allows one to exponentially propagate a population of cells in vitro, and induce differentiation when desired. This is possible with SACK cell strains and specified cell culture conditions.
SACK ASC Cell Properties
- Long-term propagation in xanthosine (Xs)-supplemented medium
- Suppressed asymmetric cell kinetics
- Express the epithelial stem cell biomarker LGR-5 and the liver stem cell biomarker EpCAM
- Xn-suppressed non-random sister chromatid segregation
- Quality controlled to determine number of actual stem cells More info
Differentiated progeny Cell Properties
- Xs-free medium, confluent monolayer, human serum-supplemented medium, serum reduction
- Loss of LGR5 and EpCAM expression
- Expression of hepatocyte-specific nuclear receptor PXR
- Albumin secretion
- Alpha-fetoprotein secretion (indicates presence of hepatoblasts)
- Inducible cytochrome P450 activity (CYP3A4)
- Secretion of hepatocyte basement membrane proteins
*Additional similar, but less well characterized, independent clonal cell strains are available. For more information, contact us.
| Product Type: | Cell Line |
| Name: | SACK-Xs 12(3) |
| Cell Type: | neonatal human liver stem cells |
| Accession ID: | CVCL_5K97 |
| Morphology: | Fibroblastoid |
| Source: | liver; 1 year old male donor cells |
| Organism: | human |
| Biosafety Level: | Bsl-1 |
| Growth Conditions: | SACK medium - DMEM (4.5mg/ml high glucose) w/ 10% dialyzed FBS and 1.5mM Xanthosine |
| Subculturing: | Passage 1:5 when cells reach approx. 80% confluence |
| Cryopreservation: | 70% DMEM (high glucose); 20% dialyzed FBS; 10% DMSO |
| Storage: | Liquid nitrogen |
| Shipped: | Dry ice |
Quality Control
_QC.jpg)
Example of stem cell quality control counting result for serial passage of the expanded neonatal human liver stem cell strain SACK-Xs 12(3) (300,000 initial total cell input). Note detection of symmetric cell division by stem cells between passages (vertical lines). Click here for more information regarding the QC process.
Express the epithelial stem cell biomarker LGR5 and the liver stem cell biomarker EpCAM.
Replacement of the SACK medium with differentiation conditions allows the expanded tissue stem cells to regain their in vivo homeostatic state of asymmetric self-renewal, which yields cells committed to tissue-specific differentiation.
- Krishnanchali Panchalingam,Laura Jacox,Benjamin D. Cappiello, and James L. Sherley. Non-Random Sister Chromatid Segregation in Human Tissue Stem Cells. Symmetry 2020, 12(11), 1868; https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12111868
- Sherley, J. L. and King, J. (2010) Methods for ex vivo propagation of somatic hair follicle stem cells. Patent No. US 7,655,465 B2.
- Jaks et al. (2008) Lgr5 marks cycling, yet long-lived, hair follicle stem cells. Nature Gen. 40, 1291-1299.
- Paré, J.-F. and Sherley, J. L. (2006) Biological principles for ex vivo adult stem cell expansion, in Curr. Top. in Devel. Biol., ed. G. Schatten, Elsevier, Inc. (San Diego), Vol. 73, pp. 141-171.
- Rambhatla et al.(2005) Immortal DNA strand cosegregation requires p53/IMPDH-dependentasymmetric self-renewal associated with adult stem cells. Cancer Res. 65, 3155-3161.
- Xia, et al. (1989) Isolation of human sebaceous glands and cultivationof sebaceous gland-derived cells in an in vitro model. J. Invest. Dermatol. 93, 315-321.
- Brazhnik K, Sun S, Alani O, Kinkhabwala M, Wolkoff AW, Maslov AY, Dong X, Vijg J. Single-cell analysis reveals different age-related somatic mutation profiles between stem and differentiated cells in human liver. Sci Adv. 2020 Jan 31;6(5):eaax2659. View article
If you publish research with this product, please let us know so we can cite your paper.