Anti-Actin-2 [mAb13a] Antibody
This mouse monoclonal antibody was generated against plant actin ACT2 and recognizes subclasses 1 and 3 of vegetative plant actins (arabidopsis ACT2, 8, 11).
Actin exists as a ubiquitous protein involved with filament formation that make up large portions of the cytoskeleton. Actin filaments interact with myosin to assist in muscle contraction as well as aiding in cell motility and cytokinesis. In vertebrates there are three groups of actin isoforms: alpha, beta and gamma. The alpha actins are found in muscle tissues and are a major constituent of the contractile apparatus. The beta and gamma actins co-exists in most cell types as components of the cytoskeleton and as mediators of internal cell motility.
From the laboratory of Richard B. Meagher, PhD, University of Georgia.
 Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
This mouse monoclonal antibody was generated against plant actin ACT2 and recognizes subclasses 1 and 3 of vegetative plant actins (arabidopsis ACT2, 8, 11).
Actin exists as a ubiquitous protein involved with filament formation that make up large portions of the cytoskeleton. Actin filaments interact with myosin to assist in muscle contraction as well as aiding in cell motility and cytokinesis. In vertebrates there are three groups of actin isoforms: alpha, beta and gamma. The alpha actins are found in muscle tissues and are a major constituent of the contractile apparatus. The beta and gamma actins co-exists in most cell types as components of the cytoskeleton and as mediators of internal cell motility.
From the laboratory of Richard B. Meagher, PhD, University of Georgia.
 Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
| Product Type: | Antibody |
| Antigen: | ArabidopsisActin (ACT2) |
| Accession ID: | Q96292 |
| Molecular Weight: | 45 kDa |
| Isotype: | IgG1 |
| Clonality: | Monoclonal |
| Clone Name: | mAb13a |
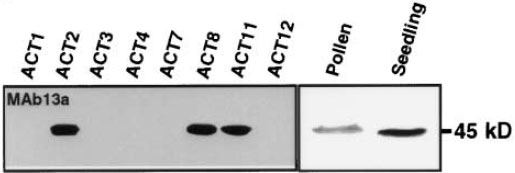
| Reactivity: | Plant actins |
| Immunogen: | Purified Arabidopsisactin (ACT2) |
| Species Immunized: | Mouse |
| Purification Method: | Protein G column |
| Buffer: | 0.1M Sodium Phosphate, pH 7.4, 0.15M NaCl, 0.05% (w/v) Sodium Azide |
| Tested Applications: | WB (1-2 ug/mL), IF |
| Storage: | -20C |
| Shipped: | Cold packs |
| Antibody | Reactivity |
| Actin [mAbGEa] | Universal |
| Actin-1 [mAb45a] | ACT1, 3, 4, 12 |
| Actin-11 [mAb2345a] | ACT1, 3, 4, 7, 11, 12 |
| Actin-2 [mAb13a] | ACT2, 8, 11 |
| Actin-8 [mAbGPa] | ACT1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 8, 11, 12 |
Western Blot Analysis
Immunofluorescence Staining Analysis

Adapted from: Kandasamy, M.K., et al. (2001) Plant Cell 13, 1541-54.
- Kandasamy, M.K., Gilliland, L.U., McKinney, E.C., and Meagher, R.B. (2001). One plant actin isovariant, ACT7, is induced by auxin and required for normal callus formation. Plant Cell 13, 1541-54.
- Kandasamy, M.K., McKinney, E.C., and Meagher, R.B. (1999). The late pollen-specific actins in angiosperms. Plant J 18, 681-91.
- Kandasamy, M.K., McKinney, E.C., Roy, E., and Meagher, R.B. (2012). Plant vegetative and animal cytoplasmic actins share functional competence for spatial development with protists. Plant Cell 24, 2041-57.
If you publish research with this product, please let us know so we can cite your paper.

![Anti-Actin-2 [mAb13a] Antibody Anti-Actin-2 [mAb13a] Antibody](https://www.kerafast.com/MediaStorage/Product/Images/Medium/778_200120200126217770D.jpg)
