Anti-Red/Green (L/M) Opsin [21069] Antibody
This IgG rabbit polyclonal was generated against the first N-terminal 38 amino acids of the bovine red/green (L/M) opsin.
Opsins are a group of light sensitive g protein-coupled receptors found in the photoreceptors cells of the retina. There are two classic types of photoreceptor cells in the retina, known as rods and cones. Rods are more numerous in the eye and are more sensitive to light and dark changes, where are cones are more sensititive to change in colors (green, red or blue). There is also a third class of photoreceptor cells (discovered later), called photosensitive ganglion cells. They do not contribute to sight but play a role in circadian rhythms and pupillary reflex.
From the laboratory of Paulo A. Ferreira, PhD, Duke University
 Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
This IgG rabbit polyclonal was generated against the first N-terminal 38 amino acids of the bovine red/green (L/M) opsin.
Opsins are a group of light sensitive g protein-coupled receptors found in the photoreceptors cells of the retina. There are two classic types of photoreceptor cells in the retina, known as rods and cones. Rods are more numerous in the eye and are more sensitive to light and dark changes, where are cones are more sensititive to change in colors (green, red or blue). There is also a third class of photoreceptor cells (discovered later), called photosensitive ganglion cells. They do not contribute to sight but play a role in circadian rhythms and pupillary reflex.
From the laboratory of Paulo A. Ferreira, PhD, Duke University
 Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
Part of The Investigator's Annexe program.
| Product Type: | Antibody |
| Antigen: | Red/Green (L/M) Opsin |
| Accession ID: | P04000, AF280398 |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Clone Name: | 21069 |
| Reactivity: | Bovine, gerbil, human and mouse |
| Immunogen: | KLH-conjugated to the first N-terminal 38 aminio acids of the bovine red/green opsin |
| Species Immunized: | Rabbit |
| Buffer: | Crude serum |
| Tested Applications: | WB, IHC (frozen, paraffin not tested), Cytochemistry (1:500), IF (1:500-1000), ELISA (Titer 15200), TEM |
| Storage: | -80C |
| Shipped: | Cold Packs (Domestic, Overnight); Dry Ice (International) |
Immunofluorescence of retina tissue sections
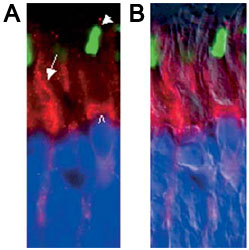
Adapted from: Mavlyutov, TA, et al. Traffic. 2002 Sep;3(9):630-40.
A)The presence of KIF5C in the myoid compartment (open arrowhead) of a red cone (ROS, filled arrowhead) through the rod photoreceptor inner segment (arrow, A) and its outer fiber. B) is an overlay of A and the same imaged by DIC. All nuclei (filled arrowheads) of red cones (Ab.21069, 1:1000) can be traced to the uppermost nuclei row of the ONL.
- Mavlyutov TA, Cai Y, Ferreira PA. Identification of RanBP2- and kinesin-mediated transport pathways with restricted neuronal and subcellular localization. Traffic. 2002 Sep;3(9):630-40.
- Cho KI, Haque M, Wang J, Yu M, Hao Y, Qiu S, Pillai IC, Peachey NS, Ferreira PA. Distinct and atypical intrinsic and extrinsic cell death pathways between photoreceptor cell types upon specific ablation of Ranbp2 in cone photoreceptors. PLoS Genet. 2013 Jun;9(6)e1003555.
- Cho KI, Patil H, Senda E, Wang J, Yi H, Qiu S, Yoon D, Yu M, Orry A, Peachey NS, Ferreira PA. Differential loss of prolyl isomerase or chaperone activity of Ran-binding protein 2 (Ranbp2) unveils distinct physiological roles of its cyclophilin domain in proteostasis. J Biol Chem. 2014 Feb 21;289(8):4600-25.
- Patil, H, Saha, A, Senda, E, Cho, K, Haque, E, Yu, M, Qiu, S, Yoon, D, Hao, Y, Peachey, N and Ferreira, PA (2014) Selective Impairment of a Subset of Ran-GTP-binding Domains of Ran-binding protein 2 (Ranbp2) Suffices to Recapitulate the Degeneration of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Triggered by Ranbp2 Ablation. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 29767-29789.
If you publish research with this product, please let us know so we can cite your paper.

![Anti-Red/Green (L/M) Opsin [21069] Antibody Anti-Red/Green (L/M) Opsin Antibody](https://www.kerafast.com/MediaStorage/Product/Images/Medium/873_200120200126258720.jpg)
